Special Issue on Federated and Transfer Learning Applications, Applied Sciences.
About this Special Issue
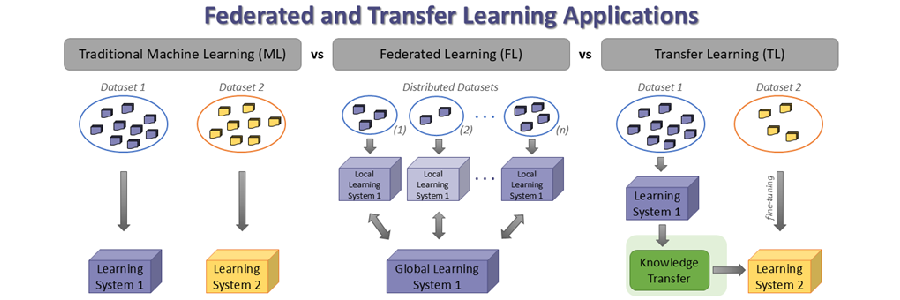
The classic example of machine learning is based on isolated learning—a single model for each task using a single dataset. Most deep learning methods require a significant amount of labeled data, preventing their applicability in many areas where there is a shortage. In these cases, the ability of models to leverage information from unlabeled data or data that is not publicly available (for privacy and security reasons) can offer a remarkable alternative. Transfer learning and federated learning are such alternative approaches that have emerged in recent years. More precisely, transfer learning is defined as the set of methods that leverage data from additional fields or tasks to train a model with greater generalizability and usually use a smaller amount of labeled data (via fine-tuning) to make them more specific for dedicated tasks. Accordingly, federated learning is a learning model that seeks to address the problem of data management and privacy through joint training with this data, without the need to transfer the data to a central entity.
In this Special Issue, we seek research and case studies that demonstrate the application of federated and transfer learning approaches to support applied scientific research, in any area of science and technology. Example topics include (but are not limited to) the following:
- Federated Learning (FL) Applications
- Distributed Learning Approaches
- Privacy-Preserving Techniques in FL
- Homomorphic Encryption Approaches in FL
- Differential Privacy Approaches in FL
- Incentive Mechanisms in FL
- Interpretability in FL
- FL with Unbalanced Data
- Selection of Appropriate FL Aggregation Function per Application
- Transfer Learning (TL) Applications
- Pre-Trained Models
- BERT-Like Models
- Federated Transfer Learning Approaches
- Applications of FL and TL in Biomedical Domain
- Applications of FL and TL in Cybersecurity
- Applications of FL and TL in Natural Language Processing
- Applications of FL and TL in Social Network Analysis
- Graph-based FL and TL
The submission deadline for this Special Issue is 20 March 2023.
Guest Editors:
- George Drosatos
Institute for Language and Speech Processing, Athena Research Center, Greece - Pavlos S. Efraimidis
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Democritus University of Thrace, Greece - Avi Arampatzis
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Democritus University of Thrace, Greece
This Special Issue is provided by the journal "Applied Sciences" and more details are available here.